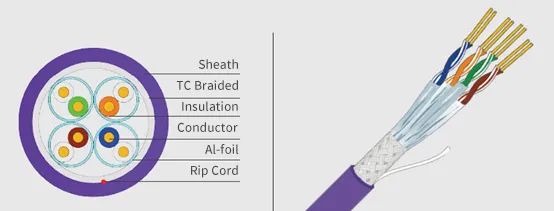
Introduction
In the rapidly advancing world of network technology, Cat 8 cable represents a significant evolution, especially when compared to its predecessors such as Cat 6 and Cat 6a. This article will delve into the functionalities and advantages of Cat 8 Ethernet cables, focusing particularly on its superiority over Cat 6, specifically the Cat 6 type b, which is known for its refined specifications catering to bulkier data transmission requirements.
What is Cat 8 Cable Used For?
Cat 8 cables, standing at the pinnacle of network cabling technology, offer phenomenal improvements in both speed and frequency. Tailored for professional and high-performance settings, these cables are indispensable in the formation of robust networking infrastructures. Below are a few primary applications:
-
Data Centers and Report Classification:
Essential for server-to-server connections, Cat 8 cables are favored in data centers for their ability to handle massive volumes of data with the CPR classification, ensuring compliance with stringent safety standards.
-
Professional Networking:
Buildings demanding high data throughput, including those needing comprehensive cables classification, rely on Cat 8 for efficient operations.
-
Enhanced Home Networking:
For those requiring high-performance gaming, intensive graphic workstations, and 4K/8K video streaming, Cat 8 is ideal, outpacing the capabilities of what is Cat6a cable used for.
Is Cat 8 Better Than Cat 6?
To determine if Cat 8 exceeds Cat 6, consider metrics like speed, frequency, and connection quality:
-
Speed and Frequency:
The Cat6a Ethernet cable wiring diagram may suggest good performance, but Cat 8 cables elevate this with speeds reaching 40 Gbps and frequencies up to 2000 MHz—leveraging enhanced bandwidths and minimal interference introduced by premium Cat 6 shielding.
-
Shielding and Safety:
Cat 8 cables often employ dual shielding techniques (Cat 6 shielded cable and Cat 6 shielded strategies included), drastically reducing signal interference and ensuring cleaner data transmission conforming to CPR cable classification standards.

-
Comparison with Other Standards:
While RS485 networks (RS485 vs Cat6) are robust for industrial environments, Cat 8′s attributes make it equally suitable for industrial and commercial applications requiring higher bandwidth and lower latency. The Cat6 cable voltage rating and classifications (CPR classification cables, class B Cat 6) further highlight the robustness of Cat 6 cables, yet Cat 8′s comprehensive capabilities are unmatched in comparison.
-
Length and Limitations:
Although limited to a 30-meter maximum effective distance, this range is well-suited for most practical implementations unlike some longer but lower efficiency types (type B Cat 6).
Conclusion
Cat 8 cables are indisputably superior for settings where ultimate performance is critical. Supporting the latest demanding applications, they reduce latency and offer unmatched quality of service. Upgrading from Cat6 class B, what is Cat 6a cable used for, to Cat 8 could be seen as a significant step towards future-proofing your network infrastructure. This choice should be guided by practical and financial considerations, aligning with the network’s needs and desired performance levels.
Further Reading and Compliance Tools: Understanding essential compliances and reports (what is a classification report, what does classification report tell us, classification certificate) is crucial. For those looking to dive deeper into the specifications and capabilities of Cat 8 versus other categories, relevant resources and industry standards should be consulted to ensure compliance and optimal selection based on the classification reports and network setup needs.
References
- Aipu Cat8 Network Cable 2000MHz Bandwidth LAN Cable Typical Speed Rate 25/40gbps All Screened Data Cable
- Outdoor Lan Cable Cat6 U/UTP Instrumentation Cable 4 Pair Solid Cable Copper Cable For Network Installation Environment
Post time: May-10-2024