cat6a utp vs ftp
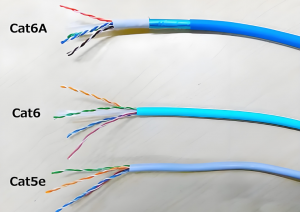
Connecting network cables can often be confusing, especially when trying to determine which of the eight copper wires inside an Ethernet cable are essential for ensuring normal network transmission. To clarify this, it is important to understand the overall function of these wires: they are designed to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) by twisting pairs of wires together at specific densities. This twisting allows the electromagnetic waves produced during the transmission of electrical signals to cancel each other out, effectively eliminating potential interference. The term "twisted pair" aptly describes this construction.
It is important to note that memorizing the T568A order isn't necessary given its decreased prevalence. If required, you can achieve this standard simply by swapping wires 1 with 3 and 2 with 6 based on the T568B configuration.
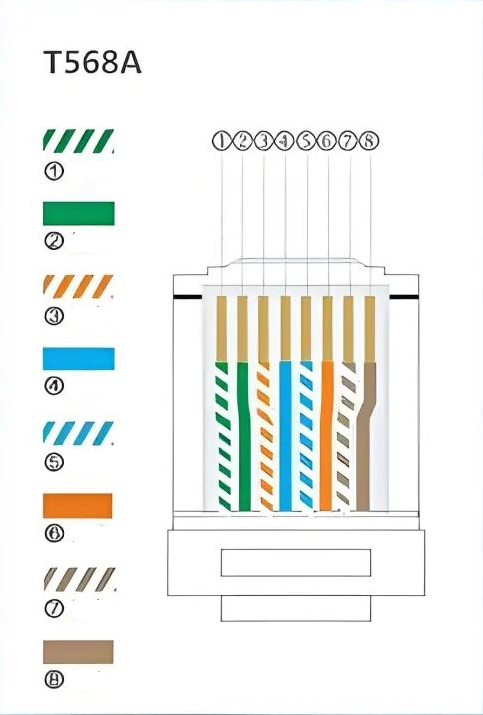
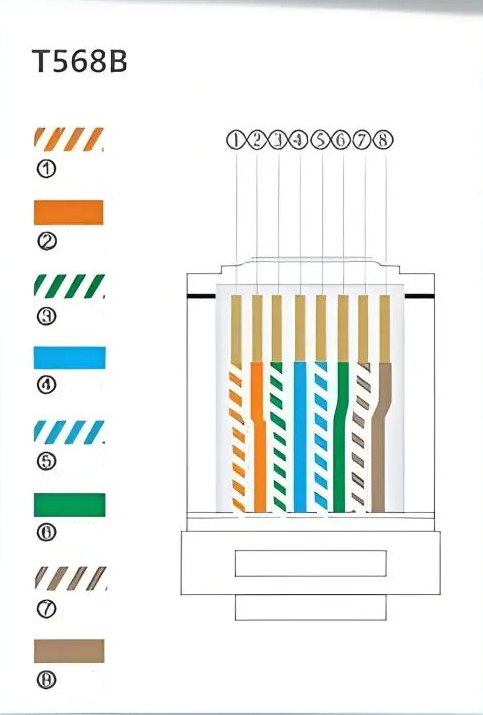
In most Fast Ethernet networks, only four of the eight cores (1, 2, 3, and 6) fulfill roles in transmitting and receiving data. The remaining wires (4, 5, 7, and 8) are bidirectional and generally reserved for future use. However, in networks exceeding 100 Mbps, it's standard practice to utilize all eight wires. In this case, such as with Category 6 or higher cables, using only a subset of the cores may lead to compromised network stability.
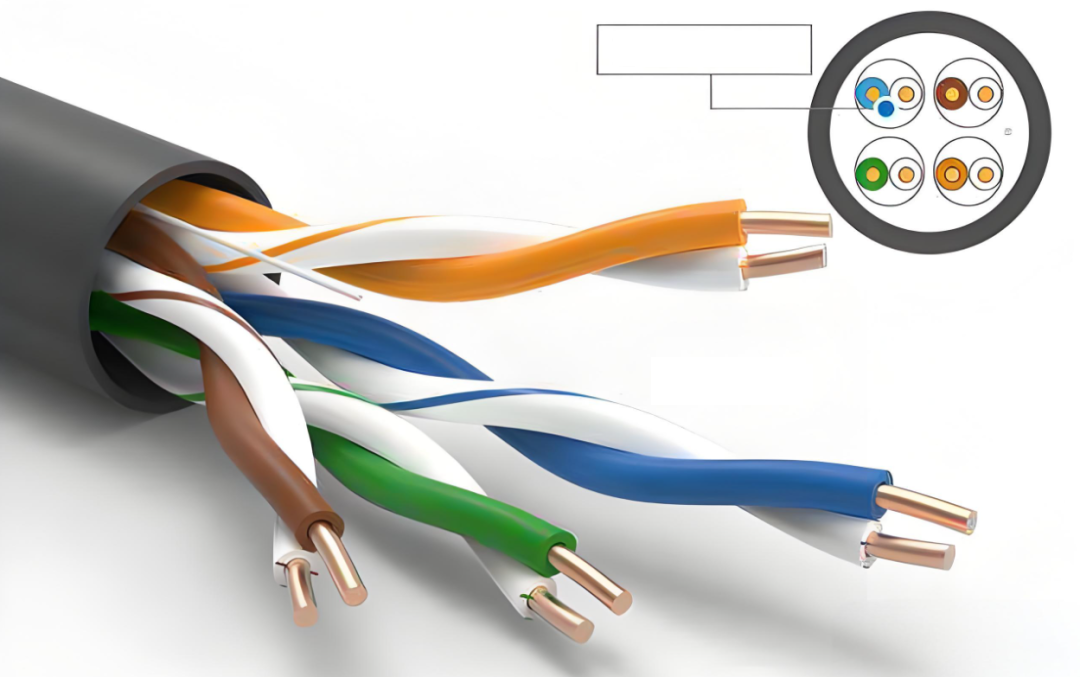
Output Data (+)
Output Data (-)
Input Data (+)
Reserved for telephone use
Reserved for telephone use
Input Data (-)
Reserved for telephone use
Reserved for telephone use

communication-cable
Module
Unshielded RJ45/Shielded RJ45 Tool-FreeKeystone Jack
Patch Panel
1U 24-Port Unshielded or Shielded RJ45
Apr.16th-18th, 2024 Middle-East-Energy in Dubai
Apr.16th-18th, 2024 Securika in Moscow
May.9th, 2024 NEW PRODUCTS & TECHNOLOGIES LAUNCH EVENT in Shanghai
Post time: Aug-22-2024
